How does the Demat account work?
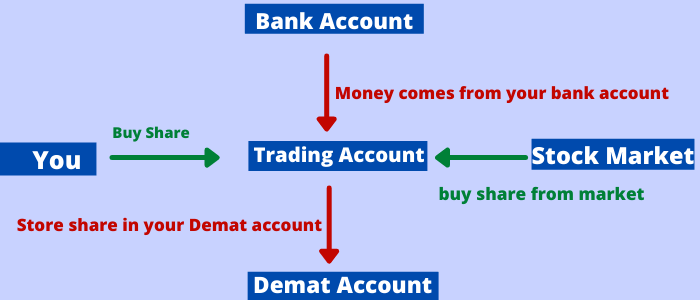
How Does Demat Account Work?: When you acquire stock in the stock market, the Share brokers deposit the shares into your Demat account. This is shown in your holdings statement. Similarly, when selling your shares, you must provide your broker with specific instructions. The shares are then sold, and the proceeds are deducted from your account. If you trade online, your Demat account will show you how many shares you sold and how much money you received.
Our Top Pick Stock Broker for Demat Account in India 2023
Upstox | Best for Beginners, Free Account Opening, & Saves from high brokerage fees. |
What is a Demat Account and How Does It Work?
A Demat account, also known as a dematerialization account, is an electronic storage and trading system for stocks, bonds, ETFs, mutual funds, and other assets. Stocks and securities were formerly only available and traded as tangible certificates, making transactions and storage inconvenient and insecure. However, when Demat accounts were established, it shortened the time necessary to clear, eliminated incidents of fraud, attracted more traders and investors, slashed brokerage prices, and dramatically boosted trading volume, in particular in the equities markets.
If you are investing or trading in shares, bonds, ETFs, and other assets, it is now compulsory to have a Demat account. Every firm listed on the stock, derivatives, and commodities exchanges must provide its securities in electronic form or Demat in the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) format.
How Does Demat Account Work?
Similar to a savings account, a Demat account operates. You can keep cash in an electronic form on the savings account with the bank, and store securities in a Demat account using an NSDL-affiliated Depository Participant (DP). The Demat account lets you keep electronically shares and securities of different businesses. You are credited to your Demat account if you purchase shares or securities and debited if you sell them.
How many types of Demat accounts are there in India?
In India, there are basically three main kinds of Demat accounts. They are as follows:
- Regular Demat Account:
This Demat account is made available to Indian residents, through intermediaries, stockbrokers, etc. This Demat account is given by depositors, such as the National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL).
- Repatriable Demat Account:
For non-resident Indian people (NRIs) wishing to invest in the Indian share market, this Demat account is beneficial. This account needs an NRE bank account connected with it. It may also have joint holders who should be Indian nationals, comparable to a standard Demat account.
- Non-Repatriable Demat Account:
Non-resident Indians can also open a Demat account. But the monies cannot be moved outside the country using this account. This account requires a corresponding NRO bank account, and NRIs may manage their funds conveniently with this account.
What is a Demat account what is its use of it?
It is quite simple to use a Demat account. By enrolling with an investment broker or sub-broker, the investor may open a Demat Account. Accessing a Demat and trading account requires an active internet connection and a transaction password when a Demat account has been opened successfully.
The first step to creating a Demat account is to pick a participant who acts as a depository agent. Following this, fill in the opening form and provide identity evidence, address certificate, pan card, and a passport-size photograph. Here you may find a full explanation of all approved documents. Once the investor agrees with the terms of the contract and the fees, an individual check-up is undertaken. A customer ID or account number is issued when the application is successfully processed. The user can use it to manage his Demat account online. An investment can then utilize this as a storage facility for the stock portfolio, to purchase and sell shares, stocks, and derivatives.
To buy or sell shares, an investor requires a trading account and a stockbroker in adding to a Demat account. The record of purchasing and selling in the individual account is usually reflected on a trade account. T+2 days are necessary to reflect the credit and debit of the shares in a Demat account after trading has taken place, and then the exchange confirmation. After the money for the purchase is paid before the date of payment, the broker is responsible for transferring shares to the investor’s Demat account.
Read About Statement of Demat Account:
A Demat is an account that holds all of a trader’s capital assets. Demat accounts, for example, store digital copies of shares, mutual funds, bonds, debentures, gold ETFs, and other assets. The account allows for simple and hassle-free asset purchase and sale operations. It is critical to review the Demat account statement regularly.
Securities acquired by Indian investors are kept in two kinds of network depositories in India. National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) and Central Depository Service Limited (CDSL) are two depository service companies.
A single document that essentially covers all the assets (equities, mutual funds, and other depository accounts) of an investor is a consolidated account statement. The CAS is a single account document. By completing the following procedures you may quickly access your CAS.
- See the portal of the CDSL.
- Choose the ‘Login’ option under the ‘Quick Links’ page.
- Enter PAN to continue.
- Add the Demat account number to continue.
- Enter details like birth date and captcha.
- Send and enter the OTP that is sent to the cellphone registered number for login.
- You can view and download your Demat account statement successfully after authentication and logging in.
More About Demat Account Statement:
The next stages assist people to understand and analyze the statements of the Demat account:
- Personal Information: Even before glancing at the account statement, one should double-check their information.
- CDSL has the following Demat Accounts: This is a list of the investor’s whole portfolio. The parts depict the breakdown of various assets such as equities, mutual funds, government securities, and so on.
- Total Portfolio Value (all investments combined): This is a list of the investor’s whole portfolio. The parts depict the breakdown of various assets such as equities, mutual funds, government securities, and so on.
- Transactions Statement: This section displays all transactions for a certain time frame.
- Holding statement: This section contains a list of all of the investor’s assets. The ISIN, security name, current balance, frozen balance, pledge balance, free balance, market price, or face value, as well as the value of the assets, are all included for stocks. The fund name, folio number, investor information, date, transaction description, amount, NAV, Price, units, stamp duty, and opening and closing balance for mutual funds are all included on the statement.
How Demat account different from a bank account?
A bank account is a place where the account holder deposits money. The account holder has the ability to withdraw funds from the bank account at any time and from any location. Also, putting money in a bank account counts as saving rather than investing.
A Demat account is a holding account for financial instruments that are held in a dematerialized or electronic version. The Demat account holds all of the stock purchases made through the trading account. The securities can only be sold during trading hours and only over the Internet. The presence of all financial securities in the Demat account indicates that the account user is investing rather than saving.
How to transfer shares from one Demat account to another online?
To transfer shares from one Demat account to another through the internet, go to the CDSL website and click on the “register online” option. Fill up the form and print it out to send to the DP. After the DP has verified the information provided, a password will be emailed to the registered email address. To transfer shares from one Demat to another, use the password.
What are the Demat account charges?
The presence of a Depository Participant is required to open a Demat account (DP). DPs are often brokerage companies or banks that provide the opportunity to create a Demat account with them. The majority of the time, DP will demand a little fee to open a Demat account. Other fees include custodian fees, annual maintenance fees (AMC), transaction fees, and demat&remat fees, in addition to account opening fees. These fees may differ from one brokerage business to the next. For more details please visit
How to find your Demat account number?
The format of a Demat account number is determined by the depository where the account is registered. If the account is with CDSL, the Demat number will be listed as beneficiary owner ID or BO ID in the CDSL letter. CDSL will be assigned a 16-digit Demat number that is entirely numerical. NSDL will send the letter, and the Demat number will likewise be 16 digits, but it will be an alphanumeric number beginning with IN.

