What is a Demat Account?: A dematerialized account is referred to as a Demat account. It’s similar to a wallet in that it stores the electronic shares you’ve purchased. It ensures that the entire process of stock trading is safe and efficient.
Open Best Demat Accounts
Upstox | Best for Beginners, Free Account Opening, & Saves from high brokerage fees. |
Investing in stock shares used to be done in tangible form. When you acquired stock, you received a share certificate, which served as confirmation of ownership. There was a lot of paperwork to deal with, as well as the possibility of receiving fraudulent shares. A Demat account was established to address these issues.
Having a Demat account allows you to buy and securely keep stocks. It’s comparable to a bank account in which you deposit money with the bank and keep track of your debit and credit balances in a bank passbook.
When you buy or sell stocks, your Demat account will be credited or debited, accordingly. It may be used to store a wide range of investments, including stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, bonds, and government securities. You may create a Demat account without owning any shares and keep your account balance at zero.
You may maintain all of your financial assets in a single electronic form with a Demat account. The basic aim of a Demat account is to hold all of the shares you’ve purchased or dematerialized (physical shares transferred to electronic format) and to make trading easier for you.
More Details Article Please visit:
What is the Meaning of a Demat Account?
A Demat account, also known as a Dematerialized account, is a type of dematerialized account. The basic purpose of a Demat account is to store electronic shares and securities. It aids you in online trading activities such as buying and selling stocks, as well as transforming real stock into electronic form. A dematerialized account holds all of the shares, mutual funds, bonds, government securities, and other investments. Investors can also use it to make intraday transactions.
Popular Discount Broker Upstox
|
What is Dematerialization?
The process of converting physical certificates to electronic certificates is known as dematerialization. In general, papers may be accessed and made available 24 hours a day. Dematerialization’s major goal is to eliminate the need for physical shares while also allowing for easy tracking and monitoring. It assists in the conversion of physical shares to electronic format.
Types of Demat accounts:
There are three types of Demat accounts:
- Regular Demat Account.
- Repatriable Demat Account.
- Non-repatriable Demat Account.
The Demat account kinds need to be understood as to why they are categorized as such. This might lead to better involvement in the stock market. Once you have learned the essentials, choosing the sort of Demat account that is most suited to you will be easy.
Regular Demat account:
For investors residing in India, a normal Demat account is required. It is suitable for people dealing with shareholdings alone. The shares that you purchase are held on the account digitally. They are removed from that which is sold. There’s no need to keep a regular account for Demat if you want to trade in future options. This is because futures and options have an expiration date and do not have to be kept.
A new form of Demat account named the basic services Demat account was recently launched by SEBI (BSDA). That’s identical to a conventional Demat account except that if the holding is within Rs 50,000 there are no maintenance expenses. For stakes ranging from Rs 50,000 to Rs 2, the fee is Rs 100 per year. The BSDA was launched to help investments who are not yet opening a Demat account but are interested in participating in the marketplace.
Repatriable Demat account:
Non-resident Indians can also participate in stock markets, along with individuals living in India. However, NRIs are unable to utilize a standard Demat account to invest, because a regular Demat account does not authorize the repatriation of funds. You can move the cash overseas using a repatriable Demat account, but you need a Non-Resident External NRE bank account for it. You must cancel the normal Demat account and transfer the holdings to a Non-Resident Ordinary Demat account if you become an NRI and have equity interests in India.
Non-repatriable Demat account:
Just like a repatriable Demat account, the non-repatriable account is designed to make a little distinction for non-resident Indians. You can move money overseas through a repatriable Demat account, but in the event of non-repatriable Demat accounts, it is not permitted to transfer cash. This is intended for NRI investors wanting to use the funds in India
Diverse accounts according to their functionality are regular, repatriable, and non-repatriable accounts The finest Demat accounts may also be divided into services. Delaminated accounts may also be divided into 2-in-1 and 3-in-1 accounts based on associated services like trader accounts and bank accounts.
For more details please visit.
Advantages of a Demat account:
Ownership and transfer of securities through electronic book entries take place within the depositary system. Holders of Demat accounts can purchase and hold shares, NCDs, or other bonds. Just like a bank account with the following benefits and security features, they have access to the account.
- There is no stamp duty on securities transfers.
- The transfer of securities immediately and quickly.
- Elimination of ‘Bad Deliveries’.
- Quick payment of Corporate Benefits such as bonuses, Rights, Dividends, etc.
- Elimination of bank and address mismatch.
- Elimination of risk by loss, theft, mutilation, etc.
- Convenient Nomination facilities.
- No Demat securities TDS deduction.
- Convenient formalities for transmission of a holder’s death.
- Customer frequently receives Demat accounts and statements.
For More Details Please Visit:
How to open a Demat account Step-by-step guide:
- Decide on a Depository Participant (DP): Which is an approved bank, bank, or broker with whom you wish to open the Demat Account? Ideally, the choice of a DP should rely on the brokerage fee, yearly fees, and levy supplied.
Send a properly completed starting account and KYC form. In addition, you must attach copies of this information.
- PAN Card
- Residence Proof
- ID Proof
- Passport-sized photographs
You must next sign an agreement stating all the rules, regulations, and rights relating to the keeping of a Demat Account. Attentively read and feel free to clear your questions. Read them carefully. When presented to the DP, the authorized person shall sign it, and you will receive a copy thereof.
When you establish an account with the DP, you will be given a unique Client ID. This, along with other information, will assist you in gaining online access to your Demat Account.
The DP will also provide you with instruction sheets that you may use for depository services like transfer, purchase, and so on.
It’s worth noting that a Demat Account doesn’t require a “minimum balance” of shares or financial securities. Additionally, you can have several Demat Accounts connected to a single PAN. Not with the same DP, though.
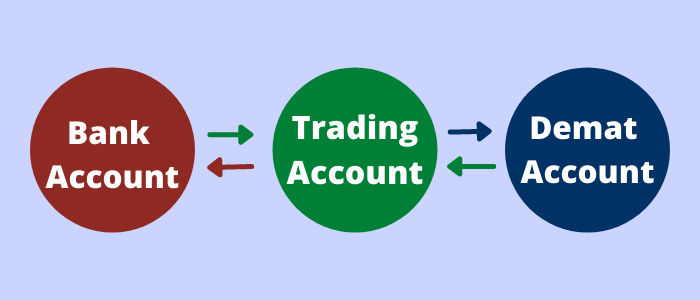
How is a Demat account different from a bank account?
A bank account is a place where the account holder deposits money. The account holder has the ability to withdraw funds from the bank account at any time and from any location. Also, putting money in a bank account counts as saving rather than investing.
A Demat account is a holding account for financial instruments that are held in a dematerialized or electronic version. The Demat account holds all of the stock purchases made through the trading account. The securities can only be sold during trading hours and only over the Internet. The presence of all financial securities in the Demat account indicates that the account user is investing rather than saving.
How to Select Best Demat Account for Trading:
To buy and store financial securities, you’ll need a Demat account. It keeps track of all of your investments in an electronic format. A Demat account is maintained by two depositories in India. The National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) and the Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL) are their names (CDSL).
Choosing a depository is the first step in setting up a Demat account. Investors have the option of choosing between the NSDL and the CDSL. Following the selection of a depository, the investor must select a Demat account. In contrast to depositories, several financial organizations provide Demat accounts. Investors are frequently perplexed as to which option to select. As a result, we’ve compiled a list of considerations to make when selecting a Demat account.
